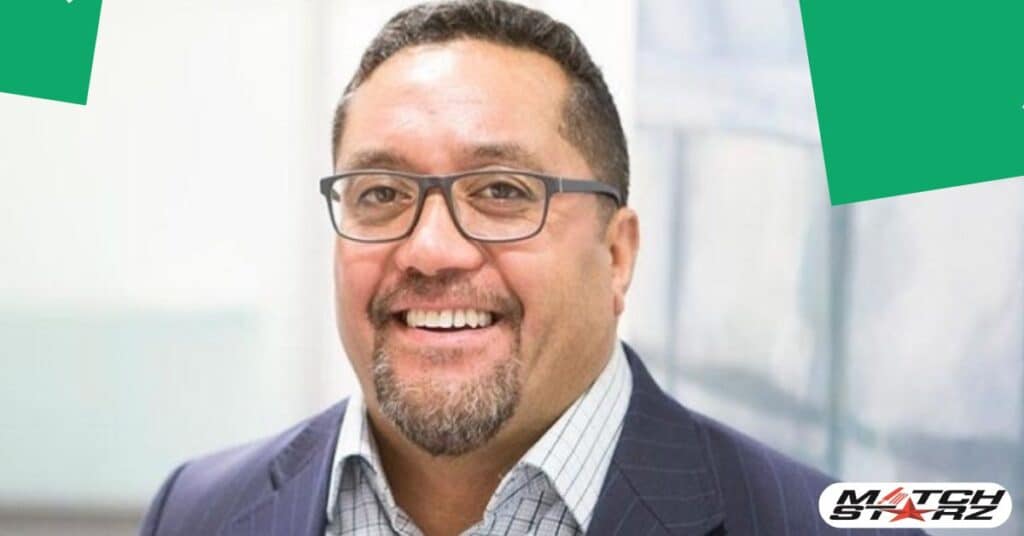
Judge Mina Wharepouri believes in justice—treating everyone fairly—and equality, ensuring all people have the same rights. These values help build a society where respect is central. Her work is driven by these important principles.
Judge Mina Wharepouri makes you wonder, what truly sets a judge apart? It’s their strong commitment to fairness and helping others. She is a perfect example of what it means to be a dedicated and just judge.
Judge Mina Wharepouri is widely recognized for her dedication to justice and fairness. She tirelessly works to ensure everyone, especially those in need, receives equal treatment. Her influence continues to inspire many in the legal world.
Historical Overview of Justice and Equality
Origins and Evolution
The concept of justice has roots in ancient civilizations, from the Code of Hammurabi to Roman and Greek legal traditions. Equality, although historically less emphasized, became a major societal goal during the Enlightenment and civil rights movements.
- Magna Carta (1215): One of the earliest documents to call for fair treatment under the law.
- US Constitution (1787): Embedded principles of justice and equality that still influence modern legal frameworks.
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948): A pivotal document asserting global standards for justice and equality.
Key Legal Milestones
Several key legal milestones have paved the way for justice and equality to coexist in modern societies:
- The abolition of slavery in the 19th century.
- Women’s suffrage movements.
- The Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s.
Justice: Fair Treatment vs. Equality: Equal Treatment
Justice guarantees fair treatment by taking into account the unique circumstances of each individual. This approach aims to deliver balanced and equitable outcomes for everyone. For example, in criminal justice, sentencing often takes into account various factors, such as intent and past behavior. Equality, on the other hand, aims to provide equal opportunities for all, regardless of background, ensuring that every person has the same access to resources, rights, and protections under the law.
How They Work Together
In practice, justice and equality often intersect. For instance, restorative justice seeks to rehabilitate offenders while promoting equality by ensuring that marginalized individuals are not disproportionately impacted by legal punishments.
Modern Legal Frameworks for Justice and Equality
National and International Law
In today’s legal systems, justice and equality are enforced through a combination of national and international laws:
- Anti-discrimination laws: Protect individuals from discrimination based on race, gender, age, or disability.
- Human rights charters: International agreements, like the UN Human Rights Council, aim to establish global standards for justice and equality.
The Role of the Judiciary
Courts play a critical role in maintaining justice and equality. Judges interpret and apply laws, often ruling on cases that determine whether justice has been served in a fair and equal manner. Judges like Mina Wharepouri exemplify the judiciary’s commitment to promoting these ideals.
Challenges to Achieving Justice and Equality
Systemic Bias
Despite legal frameworks, bias remains a challenge. Racial, gender, and economic inequalities can lead to unjust outcomes, where marginalized groups receive disproportionate treatment.
Social and Economic Disparities
In many societies, wealth and social standing influence access to legal representation, creating an imbalance in justice. Poorer individuals often struggle to access the same quality of representation as wealthier individuals, perpetuating inequality.
Legal System Limitations
Limited resources in courts, such as overcrowded dockets or underfunded public defenders, often undermine the ability of the legal system to fully ensure both justice and equality for all. As a result, many individuals may not receive the legal representation they deserve. Moreover, these constraints can lead to significant delays in legal proceedings, further affecting the overall fairness of the system.
The Role of Restorative Justice in Equality
Definition of Restorative Justice
Restorative justice is an alternative approach to criminal behavior, focusing on the rehabilitation of offenders through reconciliation with victims and the community. This method fosters community engagement and aims to address the underlying causes of criminal behavior, rather than just punishing it.
Restorative Justice and Social Healing
By focusing on repairing harm, restorative justice offers a more humane and equitable approach to justice, especially for marginalized communities. For instance, indigenous populations often prefer this method because it aligns more closely with their cultural practices of healing and community restoration. Furthermore, this approach not only addresses the needs of victims but also encourages accountability among offenders.
Notable Cases that Shaped Justice and Equality
Case Study 1: Civil Rights Movement in the US
The Brown v. Board of Education case was a landmark decision that desegregated public schools in the US, promoting racial equality in education.
Case Study 2: Gender Equality in Law
The Reed v. Reed case in the 1970s marked a pivotal moment for gender equality, ruling that arbitrary gender discrimination in law was unconstitutional.
Case Study 3: Indigenous Rights and Equality
Recent rulings in New Zealand have advanced the rights of indigenous populations, ensuring they have equal access to land and legal protections.
| Case Name | Year | Issue Addressed | Outcome |
| Brown v. Board | 1954 | Racial Segregation | Ended segregation in public schools |
| Reed v. Reed | 1971 | Gender Discrimination | Ruled arbitrary gender discrimination illegal |
| Indigenous Land Rights | 2014 | Indigenous Land Ownership | Returned lands to indigenous communities |
The Role of Judges in Promoting Justice and Equality
Judicial Activism vs. Judicial Restraint
Judicial activism refers to judges taking an active role in shaping law, often interpreting the constitution broadly to advance justice and equality. In contrast, judicial restraint advocates for a more conservative approach, allowing legislative bodies to drive legal changes.
Notable Judges and Their Contributions
Judges like Ruth Bader Ginsburg and Thurgood Marshall have gained recognition for advancing gender equality and civil rights, respectively. Additionally, Judge Mina Wharepouri, a trailblazer in justice, promotes equality, particularly for marginalized groups.
Justice and Equality in Everyday Life
Workplace Equality
Modern laws such as equal pay acts ensure that individuals are treated fairly in the workplace. Gender, racial, and age discrimination laws provide legal recourse for unfair treatment.
Criminal Justice Reform
Ongoing efforts to reform the criminal justice system aim to eliminate biases, ensuring that marginalized groups are not disproportionately affected by legal punishments.
Community-Based Solutions
Grassroots movements and community-based organizations play a vital role in promoting justice and equality at local levels, often filling gaps where the legal system may fall short.
The Global Perspective: Justice and Equality Across Borders
International Human Rights Law
The UN Human Rights Council works globally to enforce standards of justice and equality. International treaties ensure that countries work toward maintaining human rights and protecting against discrimination.
Case Study: Social Justice Movements in Other Countries
In South Africa, post-apartheid legal reforms aim to address systemic racial inequalities. Advocates have made significant progress through legal representation and restorative justice.
Challenges in Balancing Justice and Equality
When Equality Conflicts with Justice
Sometimes, the pursuit of equality may conflict with justice. For example, affirmative action policies, designed to promote equality, can sometimes be viewed as conflicting with fair treatment of all individuals.
Balancing Personal Freedoms with Social Equity
The line between protecting personal freedoms and ensuring social equity is often thin. Laws must balance these two concepts to create a just society.
The Future of Justice and Equality
Emerging Trends
New legal technologies, such as AI, are beginning to shape the future of justice and equality by reducing human error and bias in legal proceedings.
Legislative Reforms on the Horizon
Countries are beginning to introduce reforms aimed at addressing inequality in the legal system. For example, new laws focused on digital rights and restorative justice are being debated.
FAQs
What is the difference between justice and equality?
Justice focuses on fair treatment based on circumstances, while equality emphasizes equal opportunities and treatment for everyone.
How can justice and equality be improved in the legal system?
Reforming biased systems, improving access to legal representation, and embracing restorative justice can enhance justice and equality.
Why is justice important in society?
Justice ensures that individuals are treated fairly, creating a society where rights are respected and protected.
Can there be equality without justice?
True equality requires justice to ensure fair outcomes for all individuals.
What role can individuals play in promoting justice and equality?
Advocating for policy reforms, supporting community engagement, and standing up for marginalized groups are ways to promote these values.
Conclusion
Justice and equality are essential to the stability and fairness of any society. Judge Mina Wharepouri and other notable figures have made significant contributions toward achieving these ideals, promoting fair treatment and equal rights for all. As we look to the future, we must continue our efforts to ensure that justice and equality remain central to our legal systems.

Adim Smith is an experienced blogger at Match Starz, sharing in-depth insights on celebrities and athletes. With a passion for storytelling, he brings readers closer to the lives and achievements of today’s biggest stars.